Diabetic Foot Ulcers.
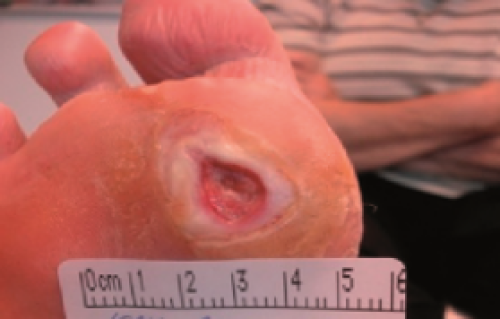
What is a diabetic foot ulcer?
Diabetic-related foot disease encompasses one or more of the following conditions occurring in the foot of an individual with either current or previously diagnosed diabetes mellitus: peripheral neuropathy, peripheral artery disease, infection, ulcers, neuro-osteoarthropathy, gangrene, or amputation. Foot ulceration stands as one of the most severe complications of diabetes, leading to diminished quality of life and imposing financial burdens on the affected individual. Furthermore, it places significant strain on the individual's family, healthcare providers, facilities, and society as a whole.
Consult IWGDF Website for more information.
Aethiology: Causes of diabetic foot ulcer and how and why it develops?
Who can get a diabetic foot ulcer and how does it start? What are the main causes of a foot ulcer in diabetic patients and how does it typically develop?
Diabetic foot ulcers can affect individuals who have either current or previously diagnosed diabetes mellitus. The main causes of foot ulcer in diabetic patients are typically due to a combination of factors:
- Nerve Damage or Neuropathy: Diabetes can lead to nerve damage which can cause decreased sensation, making it difficult for individuals to feel pain, heat, or cold. This means that individuals may not notice minor injuries like cuts and blisters or pressure points, such as those from ill-fitting shoes, which can then develop into ulcers.
- Poor Circulation: Diabetes can also lead to vascular diseases, including peripheral artery disease, which affects the blood flow to the feet. Reduced blood flow can in turn interfere with the wound healing process.
- Risk Factors: There are several risk factors that can increase the likelihood of developing a diabetic foot ulcer including poor glycemic control, smoking, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, obesity, and a history of foot problems.
Diabetic foot ulcers typically develop over time and can lead to serious complications if not treated promptly and effectively. It’s important for individuals with diabetes to regularly check their feet for any signs of injury and consult a healthcare professional if they notice anything unusual.
Click here to learn more about the causes of diabetic foot ulcers.
How to treat a diabetic foot ulcer?
Treating a diabetic foot ulcer typically involves a multidisciplinary approach. Managing DFUs may include the following steps:
- Wound Care: Proper wound care for diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) is a critical aspect of treatment aimed at promoting wound healing and preventing further wound complications, such as infection, amputation etc.
- Offloading Pressure: Relieving pressure on the ulcer is crucial for healing. This might involve using special footwear, orthotic devices, or casts to relieve pressure from the impacted area.
- Managing Blood Sugar Levels: Maintaining blood sugar levels within a desired range facilitates the healing of wounds.
- Treating Infection: It's important to monitor the ulcer for signs of infection, such as increased redness, warmth, swelling or pain.
- Improving Blood Flow: Poor circulation negatively contributes to the wound healing process.
- Nutrition: Eating a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports overall health and can aid in wound healing.
- Foot Care Education: Learning how to properly care for your feet is crucial in preventing future ulcers.
- Monitoring and Follow-Up: Regular follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider are important to monitor the progress of the ulcer and adjust treatment as needed. They can also help identify and prevent any complications early. It's crucial to note that the treatment approach varies depending on the severity of the ulcer and individual patient factors.
To alleviate the impact of diabetes-related foot disease, effective strategies are needed. These strategies should encompass preventive measures, education for both patients and care providers, standardized assessment and classification protocols, multidisciplinary treatment approaches, and persistent monitoring.
For detailed guidelines we encourage you to consult the IWGDF guidelines: practical guidelines on the prevention and management of diabetes related foot disease.
How long does it usually take for DFU to heal?
The healing time for diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) widely varies based on factors like ulcer size, depth, overall health of the patient, treatment adherence etc. Healing time can range from several weeks to months. To ensure an optimal healing time it's crucial for patients to follow healthcare provider's instructions closely.
Flaminal®in the treatment of diabetic foot ulcer
In the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers, it is essential to regularly inspect the ulcers, choose appropriate dressings to manage exudate levels and preserve a moist environment. Flaminal® serves as a primary wound dressing suitable for a variety of acute and chronic wound types, including diabetic foot ulcers. This innovative Enzyme Alginogel with a unique antimicrobial enzyme system can effectively address every stage of the wound healing process by promoting an optimal moisture balance and removing wound slough or debriding the wound. Flaminal® is available in two different formulations: Flaminal® Hydro, for slightly to moderately exuding wounds and Flaminal® Forte, For moderately to highly exuding ones.
Download our Diabetic Foot Ulcer brochure.
Full Case Reports
Here you find case studies and posters for wound treatment of different diabetic foot ulcers.